

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. How many chromatids are in each replicated chromosome 7. Next, during anaphase II, the sister chromatids are pulled to opposite ends of the cells, and the cells elongate.įinally, during telophase II, the sister chromosomes uncoil, new nuclear membranes form, and the two cells are divided again, forming four new haploid cells called gametes. Mitosis has four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Here the spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes and again align them at the middle of the new cells. Divide into four phases the reproduction process of chromosomes in plant and animal cells. During this stage the chromosomes condense once again, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and the spindle apparatus forms in each of the two new cells. The next phase of meiosis is called Meiosis II. During S-phase the DNA is replicated and this results in two chromatin fibers (known as sister chromatids). Here the spindle fibers are broken up, new nuclear membranes form, the chromosomes uncoil, and the cell divides into two daughter cells. Prior to S-phase each chromosome is a single chromatin fiber. During this stage, the microtubules, or spindle fibers, pull the homologous chromosomes apart and move them to opposite ends of the cell. (e) During the pairing of chromosomes in meiosis, the homologous chromosomes come to lie. This is followed by metaphase I where the connected pairs of chromosomes align at the middle of the cell.Īfter the pairs of chromosomes are aligned, anaphase I begins. (c) Chromosomes become visible as fine long threads - Prophase.
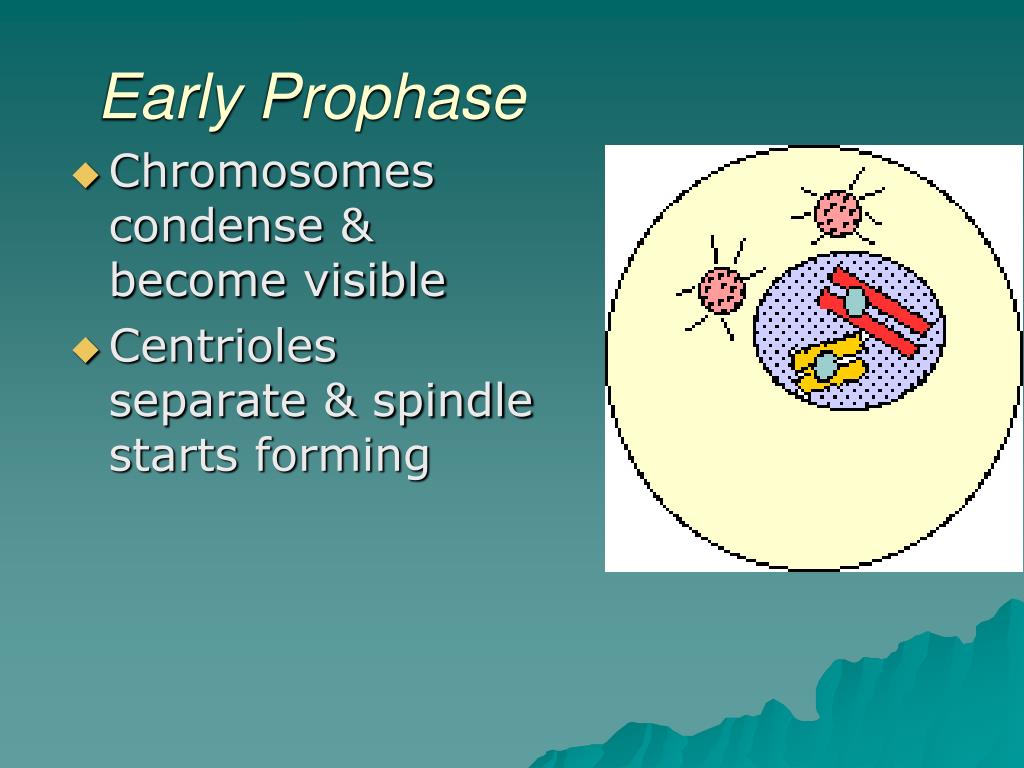
This is called recombination or crossing over. The tight pairing of the homologous chromosomes is called synapsis. As the nuclear envelope begins to break down, the proteins associated with homologous chromosomes bring the pair close to each other. duplicates of one another formed by replication during the previous S phase. During this stage the DNA condenses into chromosomes.ĭuring prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange sections of DNA. Early in prophase I, the chromosomes can be seen clearly microscopically. Prophase is characterized by the preparation of chromosomes for segregation. The first stage in Meiosis I is prophase I. In addition to the events that occur in mitotic prophase, several crucial events occur within these phases such as pairing of homologous chromosomes and the reciprocal exchange of genetic material between these homologous chromosomes.
#During prophase movie#
See the Flash movie for the following sequence of images, Prophase I is divided into five phases: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis. Thumbnail images will bring up a larger, labeled version of the


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
